Candidiasis is a fungal infection caused by Candida species, most commonly Candida albicans. These yeasts naturally live in the body without causing harm, but under certain conditions, they can overgrow and lead to infections.Candidiasis: Causes and Treatment
What Is Candidiasis?
Candida fungi are normally present in the mouth, gut, and skin, kept in check by beneficial bacteria and the immune system. However, when this balance is disrupted, Candida can multiply excessively, causing infections in different body parts.Candidiasis: Causes and Treatment
Types of Candidiasis
There are several types of Candida infections, including:
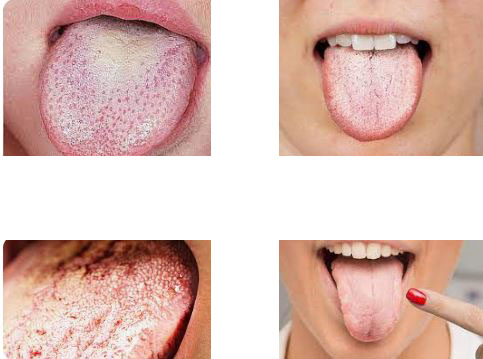
1. Oral Thrush (Oropharyngeal Candidiasis)
Manifests as white patches on the tongue and inner cheeks, sometimes causing pain and difficulty swallowing. Common in infants, the elderly, and immunocompromised individuals.
2. Vaginal Yeast Infection (Vulvovaginal Candidiasis)
One of the most common fungal infections in women, causing itching, thick white discharge, and burning during urination.Candidiasis: Causes and Treatment
3. Skin Infections (Cutaneous Candidiasis)
Occurs in warm, moist areas like armpits, groin, and under the breasts, leading to rashes and itching.
4. Nail Infections (Candidal Paronychia)
Causes swelling around the nails, discoloration, and thickening or brittleness of the nails.
5. Invasive Candidiasis (Systemic Infection)
A severe infection that spreads to the bloodstream or internal organs (kidneys, heart, brain), typically affecting people with weakened immune systems, such as HIV/AIDS patients or those undergoing chemotherapy.
Causes of Candidiasis
Several factors increase the risk of Candida overgrowth, including:
- Weakened immune system (due to diabetes, HIV, etc.)
- Antibiotic use (kills beneficial bacteria, allowing yeast to thrive)
- Hormonal changes (pregnancy, birth control pills)
- Excessive moisture (poorly ventilated skin areas)
- High-sugar diets (promotes fungal growth)
- Chronic illnesses (uncontrolled diabetes)
Symptoms of Candidiasis
Symptoms vary depending on the infection site:
- Oral thrush: White patches, soreness, difficulty swallowing
- Vaginal infection: Itching, white discharge, burning sensation
- Skin infection: Red rash, itching, irritation
- Systemic infection: Fever, chills, organ failure (in severe cases)
Diagnosis of Candidiasis
Diagnosis involves:
- Microscopic examination & culture (sampling the affected area)
- Blood tests (for systemic infections)
- Endoscopy (to examine esophageal thrush)
Treatment for Candidiasis
Treatment depends on the type and severity of infection:
1. Topical Medications
- Antifungal creams (e.g., clotrimazole)
- Vaginal suppositories for yeast infections
- Antifungal mouthwash for oral thrush
2. Oral Medications
- Fluconazole (common for most infections)
- Itraconazole or nystatin (for resistant cases)
3. Systemic Treatment (Severe Cases)
- Intravenous amphotericin B (for bloodstream infections)
Preventing Candidiasis
Reduce the risk of infection by:
- Maintaining good hygiene, especially in moist areas
- Wearing breathable cotton clothing
- Avoiding unnecessary antibiotic use
- Controlling blood sugar levels (for diabetics)
- Eating a balanced diet (low sugar, probiotics)
When to See a Doctor
Consult a healthcare provider if:
- Symptoms persist despite treatment
- Infections recur more than 4 times a year
- Signs of systemic infection (high fever, organ dysfunction) appear
Conclusion
Candidiasis is a common and usually treatable infection, but it can become serious if it spreads. Prevention focuses on maintaining microbial balance and avoiding factors that encourage fungal overgrowth. If symptoms persist, medical advice should be sought for proper treatment.

[…] summer arrives, many countries worldwide are experiencing a noticeable rise in COVID-19 cases, contrary to expectations that the virus would decline with warmer temperatures. This […]